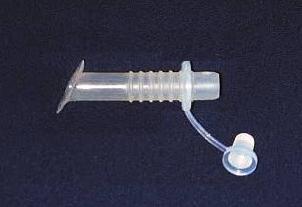
Montgomery Cannula Jackson Cannula
 ---
---
TRACH AND OSA
DEFINITIONS
By John G. Nozum
Anterior: The front part of an object.
Anesthesia: A physical state in
which
feeling is lost. It can be local, regional, or general. If
general anesthesia is used, then the person is
unconscious
for the surgery.
Anesthetic: A drug used to numb
an
area or to induce unconsciousness in order to make a
surgery tolerable by the patient.
Apnea: Cessation of breathing for at least 10 seconds.
Apnea Index (AI): Average number
of cessations in breathing lasting 10 seconds or longer
in one hour. This is one way of measuring
the severity of sleep apnea.
BiPAP: An acronym for Bi-level
Continuous
Positive Air Pressure. This is an advanced
variation of a CPAP machine, but uses different
air pressures for inhalation and exhalation.
These are used when users of CPAP machines have
difficulty breathing against the
pressure from the machine. In SOME cases, it may
reduce stomach bloating due to
swallowed air.
Button Cannula: A type of cannula
that just barely goes into the trachea and does not go
down in. A Montgomery cannula is a type of
button cannula.
Cannula: A tube that goes into an opening into the body.
Montgomery Cannula Jackson Cannula
 ---
---
Central Sleep Apnea: A condition
where the lungs receive no signal from the brain to breathe
during sleep. The loss of the “drive” to
breath
is lost for at least 10 seconds at a time.
Cork: A plug that is used to close off the opening in a cannula.
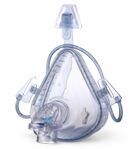
CPAP: An acronym for Continuous
Positive
Air Pressure. This is a machine that has a mask
that goes over the nose and possibly the mouth.
The unit provides increased air pressure
to help overcome obstructions that are associated
with obstructive sleep apnea. However,
these units do not work well for many patients and
tend to cause stomach bloating and
conjunctivitis.
 Please note
that
physical designs vary greatly.
Please note
that
physical designs vary greatly.
Crusts: Dried up drainage that
often
forms around a stoma, particularly around a new one
These can be swabbed off with saline solution or
a 50:50 mixture of saline solution and
hydrogen peroxide. It is usually dark brown and/or
dark red.

Cuff: An air-inflatable bulb that
some Jackson cannulas have. These generally not used
unless the patient is on a mechanical ventilator.
Note the bulb that is at the end of the cannula and is inflated.

Decannulation: The removal of a cannula. It may be intentional or accidental.
Decannulation Cap: The red cap
that
some Jackson cannula users have so that they can
close off the cannula so that they can speak and
cough normally. It is also used to wean
a person off of a tracheal cannula if he or she
has been dependent on it.
Elevation: The raising of the
head
and chest portions of the body. This sometimes helps
with obstructive sleep apnea. This is done with
a recliner chair, adjustable bed, or bed
wedge.
Encrustation: The formation of crusts around a stoma. See Crusts.
Fenestrate: To make a hole into.
USUALLY you will see quote "fenestrated," which means
that the object has a hole in it.
Fenestrator: A surgical tool used to create a lumen (hole) into the trachea.

Full Mask: A mask used with CPAP
and BiPAP machines which fits over the mouth and nose
These are needed if the person breathes primarily
through the mouth and/or has a hole in the
roof of his or her mouth going into the nasal
passage.
Granulation Tissue: Unwanted
growth
that often occurs after a recent tracheostomy. Usually,
these can be cut out without numbing, for the pain
is usually not severe.
Head Gear: A nasal or full mask
connected
to a series of straps used to hold the mask in place
during sleep. This is used with CPAP and BiPAP
machines.
Horizontal Recumbent Position: A
body position where a person is lying flat on his or her back.
It is usually the worst position for obstructive
sleep apnea.
Hypercapnia: Excessive carbon dioxide in the blood.
Hypersomnia: Prolonged or too
much
sleep. In adults, this usually means NORMALLY
sleeping more than 9-10 hours a day.
Hypopnea: Breathing that is less than normal efficiency.
Hypoxia: Unusual lack of oxygen saturation in arterial blood.
Jackson Cannula: A type of
cannula
that is curved downward and has an outer faceplate.
These require a string or trach tie to hold the
cannula in place.

Laser Assisted Uvulopalatoplasty (LAUP):
A surgery where tissues are burnt from the
throat. However, it works better at reducing
or eliminating snoring than sleep apnea.
Lidocaine: A drug commonly
injected
in the neck area to numb the area for a tracheotomy or
tracheostomy if no general anesthesia is used. While
this stuff works well, it tends to sting
when injected.
Lumen: A hole in a tube. After a tracheostomy, there is a lumen in the front of the tracheal wall.
Mandibular Advancement: A major surgery where the lower jaw is pulled forward.
Mandibular Maxillary Osteotomy and Advancement
(MMOA): A major surgery dealing with
the jaws.
Mature Tract: A surgically made
path
from the outside to the trachea which is well established.
It takes at least about three weeks to get a mature
tract. This is required for some types of
cannulas. However, ANY cannula in place will help
a tract become mature.
Micro-arousal: An episode where a
sleeper partially awakes, but is not aware of it. This is
typical during apnea events, and this greatly
reduces
sleep quality.
Micro-sleep: A situation where a person dozes off for no more than a few seconds.
Mixed Sleep Apnea: A form of
sleep
apnea where the airway gets obstructed, AND the person
temporarily loses the “drive” to breathe during
sleep. This is the worst form of sleep
apnea.
Montgomery Cannula: A type of
cannula
that is straight. These are very well suited for severe
sleep apnea that does not respond well to other
methods of treating it.

Mucous Plug: A ball or mass of
gook
that can form in a tracheal cannula. These hinder the per-
formance of a cannula. In cases where people are
TOTALLY dependent on a tracheal
cannula for breathing, these can be deadly and must
be removed swiftly, preferably by
suctioning. Most mucous plugs are either green or
white.
Multiple Sleep Latency Test (MSLT):
This is a day long test where a patient is given
periodic opportunities to snooze while wired up
to sleep monitors, such as EEG, EKG,
pulse oximeter, and more. It is used to
measure
daytime sleepiness over the course of
a day, usually the course of a standard
workday.
Like a normal sleep study, it is
completely noninvasive.
Nasal Cannula: An oxygen cannula
that has two small prongs that go slightly into the nose.
It is used when nocturnal oxygen is needed.

Nasal Mask: A mask used for CPAP and BiPAP machines that fits over just the nose.

Nebulizer: A device that adds humidity and possibly medication to a tracheal cannula.
New Tract: A surgically made path
from the outside into the trachea, which is still new (under
three weeks old).
Nocturnal: Having to do with nighttime.
Non-REM Sleep (or NREM): Sleep
that
has little or no dream activity and is characterized
by slow brainwaves. This normally makes up
around 80% of a person’s sleep.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A
medical
disorder where the airway gets obstructed during sleep
This is due to relaxation of muscles in the throat
area during sleep. Obese people and
those with throat abnormalities are at risk for
this disorder.
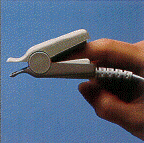
Obturator: An insertion tool used for insertng a Jackson cannula.

OSA: An acronym that stands for Obstructive Sleep Apnea.
Oxygen Concentrator: A machine
that
uses oxygen from room air and concentrates it to a nearly
pure form for nocturnal use or when supplemental
oxygen is required.

Oxygen Saturation: Proportion of
oxygen in the arterial blood. This should be at least 90%.
Young healthy people normally have an oxygen
saturation
of around 95 –97 percent.
O2: Oxygen.
Patency: Functionality of a cannula.
Patent (adjective): Functional as intended. This usually refers to cannulas.
Polysomnogram: A test where a
patient
sleeps while having his or her EEG, EKG, EMG,
oxygen saturation, and respiration monitored and
recorded. It is usually noninvasive
and extremely safe. The most uncomfortable
part is the scrubbing in order to prepare
areas of the head for EEG and EMG monitoring.
Posterior: The back part of an object.
PO2: Abbreviation for Partial Oxygen in the blood. A PO2 value less than 60 can be dangerous.
Prone Position: A body position
where
a person lies on his or her stomach. It is sometimes
the best position to use for obstructive sleep
apnea.
Pulse Ox: A slang abbreviation for pulse oximeter.
Pulse Oximeter: A device for
painlessly
monitoring oxygen saturation. It normally consists
of an electronic sensor that goes on a finger and
a unit that shows and possibly records
the oxygen saturation. This device is EXTREMELY
safe to use and can be used at home
if necessary.
 -------------
-------------
SaO2: Saturation of oxygen in the arterial blood.
Shiley: A brand of Jackson
cannula.
These are plastic as opposed to metal. See Jackson
cannula.
Silicon: A type of plastic used to make some tracheal cannulas.
Sleep: A form of rest where
awareness
of the surroundings is temporarily lost. Bodily repair
also normally occurs at this time. Most adults
need about 7-8 hours of this each day or
night.
Sleep Apnea: A medical disorder
where
breathing stops during sleep. It can be quote "central"
or "obstructive" or even "mixed." Central sleep
apnea results from lack of diaphragm move-
ment during sleep. This can be deadly. Obstructive
sleep apnea results from the airway
getting obstructed, either due to fatty tissue
and/or
physical abnormalities in the throat.
In rare and severe cases, it can be fatal.
Sleep Cycle: A period that
includes
all the stages of sleep before repeating. These
generally last around 45-90 minutes each.
Sleep Hygiene: Things that
improve
sleep quality. These include regular bedtime and
waking hours, abstinence from alcohol and caffeine,
good nutrition, and regular
exercise (not too close to bedtime).
Sleep Stage: A phase of sleep
that
has a set of characteristics. There are 5 stages in one
sleep cycle. Stage 1 is light
sleep.
Stage 2 is deeper than stage 1, but is still rather
light. Stage 3 is deeper and more restful
sleep. Stage 4 is very deep and restful
sleep. Stage 5 or REM sleep is characterized
by dream activity and rapid eye
movement. Sufferers of sleep apnea spend very
little time, if any, in stages 3 and 4,
but spend a lot of time in stages 1 and 2.
Sleep Study: An overnight test
where
a person sleeps while connected to various monitors,
such as EKG, EEG, EMG, pulse oximeter, and more.
These tests are painless (except for
the scrubbing used during prepping), unless a
special
"balloon" has to be implanted into
the throat (rarely done due to the major
discomfort).
Slow Wave Sleep: This refers to
quote
“stage 3” or “stage 4” sleep. This is where the
brainwaves are the slowest and the sleep is most
beneficial. Sufferers of sleep apnea have
little or no slow wave sleep. They tend to
spend a lot of time in stage 1 or stage 2, which
is not near as beneficial.
Somnolence: Sleepiness.
Speaking Cap: A cap placed on the
front of a tracheal cannula. See Cork and Decannulation
Cap.
Speaking Valve: A one-way valve
that
some Jackson cannula users have. It allows air in, but
not out. It allows some benefit of the cannula,
but also facilitates speech.
SpO2: Spot oxygen
saturation.
This is a quick and painless method of obtaining oxygen saturat-
ion levels, which uses a pulse oximeter.
Stenosis: A narrowing of a body
cavity
or in a tube. Many people with a tracheal stenosis re-
quire a tracheostomy.
Stoma: A surgically made
long-term
or permanent hole into the body that is not intended by
nature.
Supine Position: A body position
where a person is lying flat on his or her back. It is usually
the worst position for obstructive sleep apnea.
Titration: A process of
regulating
pressure(s) on a CPAP or BiPAP machine during a sleep
study in order to find the minimum force(s) needed
to counteract sleep apnea.
Tongue Advancement: A surgery
where
the tongue is pulled forward. This is usually
done by taking some muscle or fascia fibers and
making a “sling” that pulls the
tongue toward the front of the neck. This
fiber is buried in the tongue and chin,
and creates a V-shaped groove in the tongue.
It is designed to enlarge the airway.
However, it shows more promise at reducing snoring
as opposed to correcting
obstructive sleep apnea.
Trach: A slang word having to do
with the trachea or a tracheal cannula. It may be an adjective,
noun. or even a verb.
Trachea: Medical term for windpipe.
Tracheal: Having to do with the windpipe.
Tracheostomy: A surgery for
creating
long-term or permanent opening into the trachea. It is
sometimes used for severe obstructive sleep apnea
when other measures do not work well
and/or have severe side effects.
Tracheotomy: An emergency
surgical
procedure where an opening is made into the trachea.
These are usually short-term.
Trach Tie: A string or strap used to hold a Jackson cannula (or any of its variants) in place.
Uvula: A flap in the throat. This is sometimes the culprit in obstructive sleep apnea.
Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP):
A surgery where tissues in the throat are cut away in
order to alleviate or eliminate sleep apnea.
However, it is not particularly effective.