|
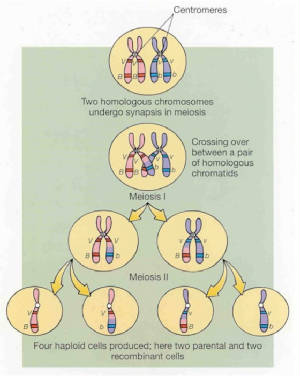
meiosis link
Remember meiosis reduces the number of chromosomes from 2n - n. This allows for gametes to unite during fertilization
preserving the correct number of chromosomes.
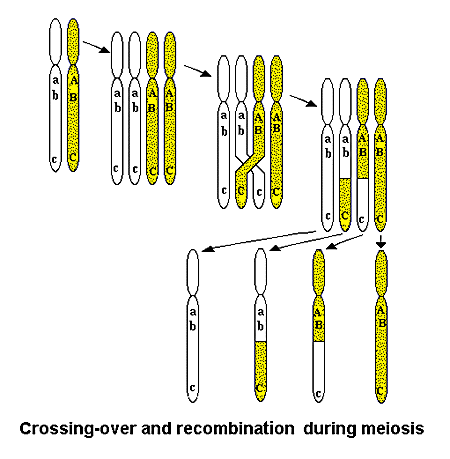
Crossing over occurs in meiosis in order to shuffle up genetic information. This is designed to creat genetic variation.
Because of crossing over and genetic variation--not two gametes are alike. This is why you are not identical to your
siblings. Specie diversity proves to be an evolutionary advantage.
Crossing over link
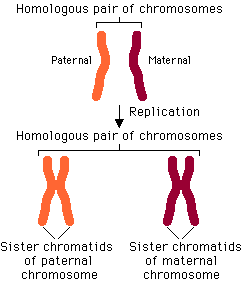
Homologous chromosomes
In diploid (2 n) organisms, the genome is composed of homologous chromosomes. One chromosome of each homologous pair comes from the mother (called a maternal chromosome) and one comes from the father
(paternal chromsosome).
|
